A battle as old as the technologies themselves: ultracapacitors and batteries rule the energy storage industry, fighting for a place at the top.
Batteries, of course, are the ubiquitous energy storage technology powering everything from electric vehicles to cell phones, but ultracapacitors are gaining market share more and more, pushed on by the increases in energy density.
Ultracapacitors and batteries differ in one significant way: ultracapacitors store energy in an electrostatic field and batteries store energy as part of a chemical reaction. Now, if you just need to power your flashlight, you can buy a set of Alkaline batteries and go on your merry, well-lit, way.
But if your application is more complex and has more demanding requirements, it's vital to understand the characteristics of each technology.
Ultracapacitors are what's known as fast energy storage and:
- have a high power density, meaning they can provide very high currents (thousands of Amperes) during a short time (ideally, less than 10 seconds)
- charge and discharge very quickly (in seconds)
- have a lifetime of over 1 million charge-discharge cycles
- have very low internal resistance (a few tenths of a milliohm) and work close to 100% efficiency
- are significantly lighter than batteries for high power applications
- have a high tolerance for extreme temperatures and work at close to full efficiency even at -40 degrees Celcius/Fahrenheit
- don’t contain harmful chemicals or toxic metals
- will not explode or burn
- have a significant leakage current, meaning they discharge if not used
Batteries are known as slow energy storage and:
- have much higher energy density, meaning they can operate for a long time, from hours to days to even years
- charge and discharge slowly (generally several hours, but depending of course on the size and type of the battery)
- usually have a lifetime of about 2000-5000 charge-discharge cycles, sometimes longer, depending on how they have been treated and the type of the battery
- have an efficiency of about 70 to 80% which results in heat that requires dissipation
- do no like to be pushed hard during charging or discharging - fast charging shortens the lifetime of batteries
- sensitive to overcharging and 0% charged stated
- have a very low leakage current
- operate poorly in very cold or hot temperatures
- contain toxic and environmentally harmful chemicals.
- can be a fire hazard, because some batteries can explode in extreme circumstances or due to physical damage
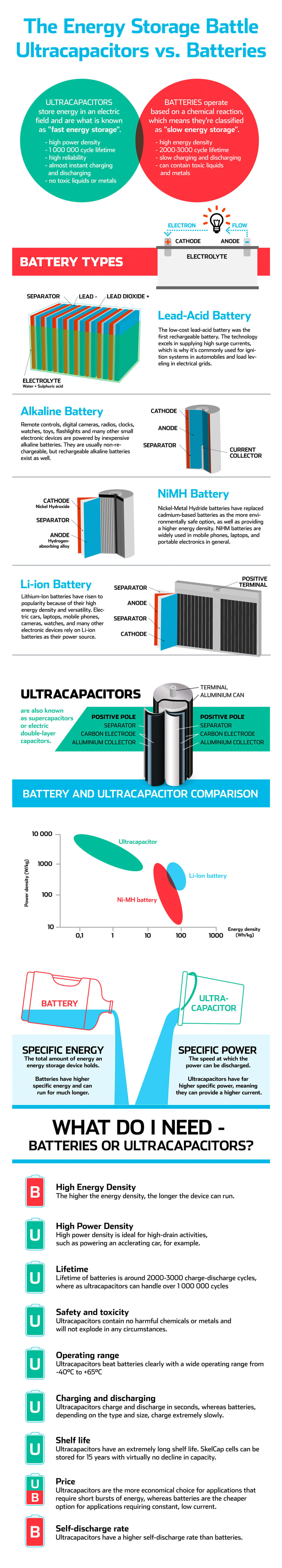
Batteries and supercaps both have their uses, but are actually complementary technologies, ideal for many applications in grid, automotive, and transportation. Batteries provide the long-term energy, whereas ultracapacitors take care of the high peaks of power and fast response.
The infographic above gives a basic understanding on the technologies behind ultracapacitors and the most widely available battery types, and provide you with the knowledge to make the decision on what's best for your needs.